PHIL 201 Quiz 7
PHIL 201 Quiz 7 Liberty University
PHIL 201 Quiz 7 God and Evil
Module 7 Week 7
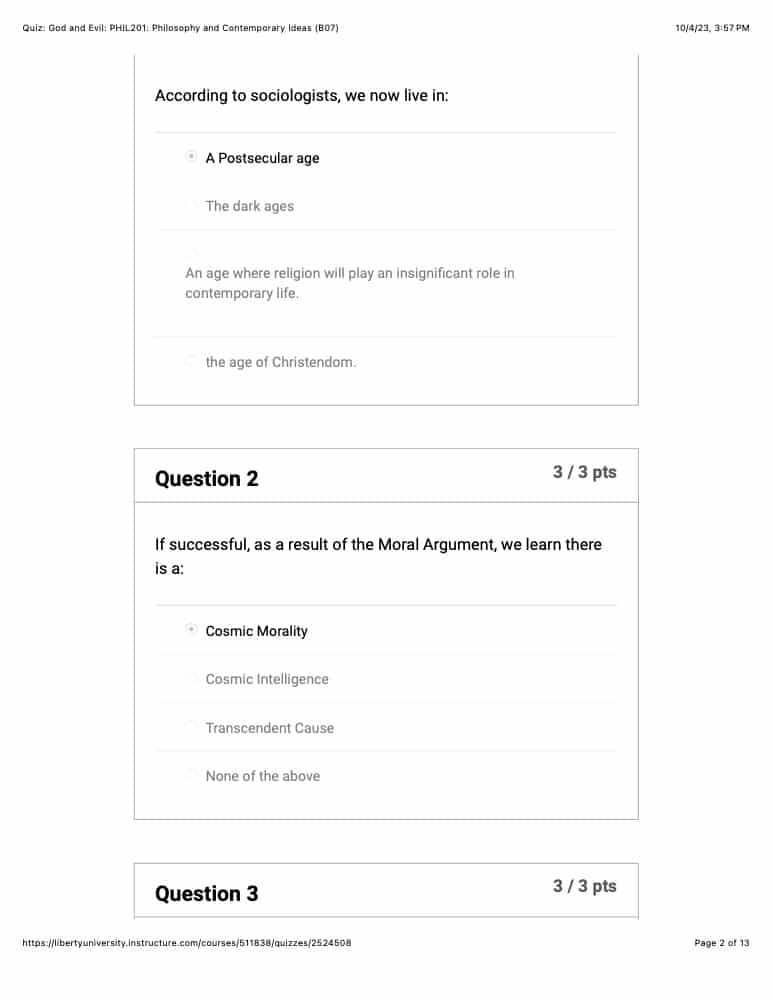
- According to sociologists, we now live in:
- If successful, as a result of the Moral Argument, we learn there is a:
- David Hume thought the teleological argument was successful in showing that the Christian God exists.
- Which argument for God is Anselm of Canterbury most-known for?
- The “multiverse hypothesis” is a prominent objection to the moral argument.
- Humans by nature worship that which is considered ultimate.
- According to the Kalam Cosmological Argument:
- William Paley’s famous “Watch maker” argument is an example of which kind of argument for God?
- According to William Lane Craig, the expansion of the universe provides evidence for the eternality of the universe.
- If successful, as a result of the teleological argument we learn that there is a:
- According to the philosopher Stephen Evans, the evidence for God is:
- If successful, as a result of the Cosmological Argument, we learn there is a
- If successful, the Kalam Cosmological Argument rules out:
- There is only one version of the problem of evil.
- God can do the logically impossible.
- As a response to the evidential problem of evil, if one argues “here is God’s reason for permitting evil,” they are providing:
- The logical problem of evil attempts to show which of the following?
- According to Richard Gale, evil is an “ought not to be, an Oh No!”
- Sometimes “noseeum” inference are good inference, sometimes they are not.
- According to the evidential problem of evil, probably, pointless evil exists.
- Which version of freedom does Plantinga’s Free-Will Defense utilize?
- As a response to the evidential problem of evil, if one argues “there is a morally sufficient reason for God’s permitting evil, we just can’t know it in all cases,” they are providing what the textbook calls:
- To claim “there is nothing God can’t do” is problematic, according to our reading on evil, for what reason?
- The evidential problem of evil attempts to show which of the following?
- Which of the following thinkers famously advanced the “soul- making” theodicy:
Other sets
- If successful, the Kalam Cosmological Argument rules out:
- The scientist Lawrence Krause has recently shown how a universe can in fact come into being out of literally nothing.
- Humans by nature worship that which is considered ultimate.
- According to sociologists, we now live in:
- Many people today think that Darwinism best explains the apparent design found in nature.
- If successful, as a result of the teleological argument we learn that there is a:
- The low entropy state of the initial universe is an example of ne- tuning.
- According to the Kalam Cosmological Argument:
- The Cosmological Arguments for God begin by considering which phenomenon?
- According to William Lane Craig, the expansion of the universe provides evidence for the eternality of the universe.
- David Hume thought the teleological argument was successful in showing that the Christian God exists.
- If successful, as a result of the Moral Argument, we learn there is a:
- If successful, as a result of the Cosmological Argument, we learn there is a
- Which of the following are reasons God might hide, even from believers for a time?
- Which version of freedom does Plantinga’s Free-Will Defense utlize?
- God never hides.
- Skeptical Theism is the view that one is skeptical of God’s goodness as a reply to the evidential problem of evil.
- Given the doctrine of original goodness, it is plausible to think that there is no reasonable nonbelief.
- There is only one version of the problem of evil.
- As a response to the evidential problem of evil, if one argues “here is God’s reason for permitting evil,” they are providing:
- The problem of divine hiding is only a problem for nonbelievers.
- According to Richard Gale, evil is an “ought not to be, an Oh No!”
- The logical problem of evil attempts to show which of the following?
- There is nothing God can’t do.
- As a response to the evidential problem of evil, if one argues “there is a morally sucient reason for God’s permitting evil, we just can’t know it in all cases,” they are providing what the textbook calls:
Set 1
- If successful, as a result of the Cosmological Argument, we learn there is a
- Which argument for God is Anselm of Canterbury most-known for?
- According to David Hume, God is best defined as “the greatest conceivable being.”
- David Hume thought the teleological argument was successful in showing that the Christian God exists.
- According to sociologists, we now live in:
- The “multiverse hypothesis” is a prominent objection to the moral argument.
- According to William Lane Craig, the expansion of the universe provides evidence for the eternality of the universe.
- The scientist Lawrence Krause has recently shown how a universe can in fact come into being out of literally nothing.
- The low entropy state of the initial universe is an example of fine-tuning.
- If successful, the Kalam Cosmological Argument rules out:
- Alvin Plantinga has developed a modalized version of the ontological argument that he thinks is at least as good as any argument in philosophy.
- Many people today think that Darwinism best explains the apparent design found in nature.
- According to the philosopher Stephen Evans, the evidence for God is:
- There is nothing God can’t do.
- The evidential problem of evil attempts to show which of the following?
- Which version of freedom does Plantinga’s Free-Will Defense utlize?
- As a response to the evidential problem of evil, if one argues “here is God’s reason for permitting evil,” they are providing:
- Sometimes “noseeum” inference are good inference, sometimes they are not.
- According to the evidential problem of evil, probably, pointless evil exists.
- Which of the following are reasons God might hide, even from believers for a time?
- The emotional problem of evil concerns how to comfort those who think belief in God is incoherent.
- It is logically possible for God to cause humans to freely act in certain ways.
- Given the doctrine of original goodness, it is plausible to think that there is no reasonable nonbelief.
- In response to the logical problem of evil, Alvin Plantinga famously has developed:
- The problem of divine hiding is only a problem for nonbelievers.
Set 2
- According to William Lane Craig, the expansion of the universe provides evidence for the eternality of the universe.
- According to the Kalam Cosmological Argument:
- Many people today think that Darwinism best explains the apparent design found in nature.
- If successful, the Kalam Cosmological Argument rules out:
- William Paley’s famous “Watch maker” argument is an example of which kind of argument for God?
- The “multiverse hypothesis” is a prominent objection to the moral argument.
- The low entropy state of the initial universe is an example of fine-tuning.
- Humans by nature worship that which is considered ultimate.
- David Hume thought the teleological argument was successful in showing that the Christian God exists.
- According to the argument from fine-tuning that is given in the textbook:
- According to David Hume, God is best defined as “the greatest conceivable being.”
- If successful, as a result of the Cosmological Argument, we learn there is a
- According to the philosopher Stephen Evans, the evidence for God is:
- The emotional problem of evil concerns how to comfort those who think belief in God is incoherent.
- There is only one version of the problem of evil.
- The logical problem of evil attempts to show which of the following?
- Which version of freedom does Plantinga’s Free-Will Defense utlize?
- God can do the logically impossible.
- As a response to the evidential problem of evil, if one argues “here is God’s reason for permitting evil,” they are providing:
- Skeptical Theism is the view that one is skeptical of God’s goodness as a reply to the evidential problem of evil.
- In response to the logical problem of evil, Alvin Plantinga famously has developed:
- Which of the following are reasons God might hide, even from believers for a time?
- God never hides.
- Given the doctrine of original goodness, it is plausible to think that there is no reasonable nonbelief.
- It is logically possible for God to cause humans to freely act in certain ways.
Set 3
- Which argument for God is Anselm of Canterbury most-known for?
- David Hume thought the teleological argument was successful in showing that the Christian God exists.
- The Cosmological Arguments for God begin by considering which phenomenon?
- According to William Lane Craig, the expansion of the universe provides evidence for the eternality of the universe.
- The scientist Lawrence Krause has recently shown how a universe can in fact come into being out of literally nothing.
- If successful, as a result of the teleological argument we learn that there is a:
- According to David Hume, God is best defined as “the greatest conceivable being.”
- According to the argument from fine-tuning that is given in the textbook:
- Many people today think that Darwinism best explains the apparent design found in nature.
- The “multiverse hypothesis” is a prominent objection to the moral argument.
- Humans by nature worship that which is considered ultimate.
- If successful, as a result of the Moral Argument, we learn there is a:
- According to the philosopher Stephen Evans, the evidence for God is:
- Sometimes “noseeum” inference are good inference, sometimes they are not.
- According to Richard Gale, evil is an “ought not to be, an Oh No!”
- It is logically possible for God to cause humans to freely act in certain ways.
- Which of the following are reasons God might hide, even from believers for a time?
- According to the evidential problem of evil, probably, pointless evil exists.
- God never hides.
- As a response to the evidential problem of evil, if one argues “here is God’s reason for permitting evil,” they are providing:
- Which of the following thinkers famously advanced the “soul-making” theodicy:
- The problem of divine hiding is only a problem for nonbelievers.
- The emotional problem of evil concerns how to comfort those who think belief in God is incoherent.
- There is nothing God can’t do.
- Which version of freedom does Plantinga’s Free-Will Defense utlize?