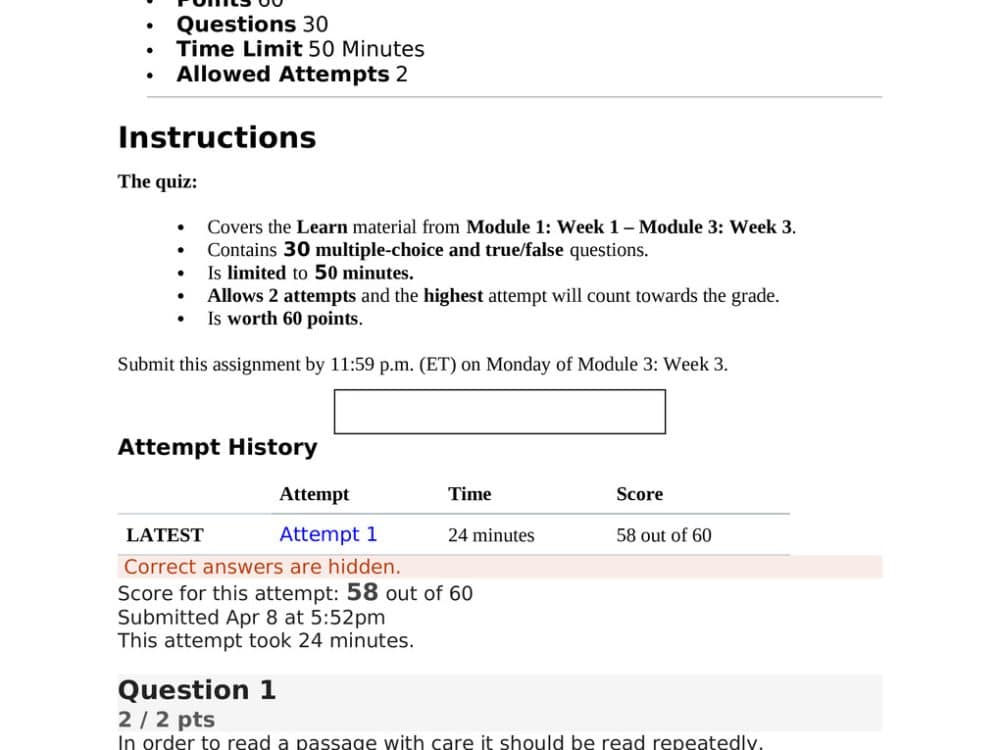
BIBL 360 Quiz 1
BIBL 360 Quiz 1
BIBL 360 Quiz: Observation, Principles of Structure, and Interpretation
- _______________ is the method of writing.
- Observation is simply knowing
- Application asks
- ___________________ brings meaning to the facts.
- The question of “___________” addresses the purpose of the passage or book.
- The gathering together of main ideas by the author in order to clarify his thoughts is known as summary.
- The book of ___________ uses the structural device of “question posed.” Here Paul leads his readers through his theological assertions by using questions.
- deals with the understanding or meaning of the inspired Word of God.
- Careful observation guarantees accurate interpretation.
- Luke 1–3 weaves together the stories of John the Baptist and Jesus. This is the principle of structure known as
- Which of the following is not one of the five C’s of interpretation?
- When you are observing a whole passage you should read the passage with care, record your initial impressions, and record the major facts.
- can be defined as the ministry of the Holy Spirit which makes clear the truth of the written revelation of the Bible.
- The tone of the passage is something to consider when interpreting the “___________” of a passage.
- The principle of structure where altering or exchanging certain elements in the text so that the reader is moving back and forth between several ideas is known as
- is the goal of Bible study. It is not enough for us to understand Scripture; God wants us to be changed by it.
- In interpretation, stating the initial proposal based on the content allows you to test your hypothesis as your work through the other stages of interpretation.
- An outline, diagram, or chart can bring the structure of a passage into focus.
- Psalm 1:1–3 speaks of the righteous man. Psalm 1:4–6 speaks of the unrighteous man. The structural devices used in these six verses is
- This major fact would attempt to identify a point in the history of Israel or the church.
- Which of the following is not one of the five C’s of interpretation?
- Observation asks
- Observing a landmark can be an important part of observing the “where.”
- Observing important words, verb tense, command, etc. is part of observing the “what.”
- The pivot point in the life of Kind David is when
- When observing the characters in a passage, the characters indirectly involved in the action are inconsequential.
- Duration of the action is an important “where” consideration.
- is simply the gathering of all the facts of who, what, where, and when.
- Drawing conclusions based on your study of the facts is the process of
- The Bible was written across the continents of Asia, Europe, and Africa.
Set 1
- When you read the passage with care you are reading ____________.
- ______________ deals with the content of the Bible.
- Drawing conclusions based on your study of the facts is the process of
- Careful observation guarantees accurate interpretation.
- The principle of structure that briefly restates the main ideas presented is known as
- The question of “___________” addresses the purpose of the passage or book.
- Luke 1–3 weaves together the stories of John the Baptist and Jesus. This is the principle of structure known as
- The pivot point in the life of Kind David is when
- Psalm 1:1–3 speaks of the righteous man. Psalm 1:4–6 speaks of the unrighteous man. The structural devices used in these six verses is
- Duration of the action is an important “where” consideration.
- Which of the following is not a principle to keep in mind when you ask questions of interpretation?
- is the goal of Bible study. It is not enough for us to understand Scripture; God wants us to be changed by it.
- The Bible was written across the continents of Asia, Europe, and Africa.
- This major fact would attempt to identify a point in the history of Israel or the church.
- Observing important words, verb tense, command, etc. is part of observing the “what.”
- What is the second step in the process of observation?
- ________________ is simply the gathering of all the facts of who, what, where, and when.
- When you read the passage with care you are reading ____________.
- The question of purpose is two-sided since it addresses
- The gathering together of main ideas by the author in order to clarify his thoughts is known as summary.
- _______________ deals with the understanding or meaning of the inspired Word of God.
- Observing a landmark can be an important part of observing the “where.”
- When observing the characters in a passage, the characters indirectly involved in the action are inconsequential.
- Observation asks
- In order to read a passage with care it should be read repeatedly.
- Interpretation asks
- Application asks
- The principle of structure where altering or exchanging certain elements in the text so that the reader is moving back and forth between several ideas is known as
- What is the third step in the process of observation?
- can be defined as the ministry of the Holy Spirit which makes clear the truth of the written revelation of the Bible.
Set 2
- Observation is simply knowing
- Galatians 6:7–8 says, “Do not be deceived: God cannot be mocked. A man reaps what he sows. The one who sows to please his sinful nature, from that nature will reap destruction; the one who sows to please the Spirit will reap eternal life.” This is an example of
- The pivot point in the life of Kind David is when
- Comparison is associating things that are opposite.
- is simply the gathering of all the facts of who, what, where, and when.
- Which of the following is not a principle to keep in mind when you ask questions of interpretation?
- A structural outline shows the logic in a passage by writing it out in paragraph form rather than verse form.
- The gathering together of main ideas by the author in order to clarify his thoughts is known as summary.
- This major fact seeks to identify all the principle characters in the passage.
- Which of the following is not one of the five C’s of interpretation?
- In order to read a passage with care it should be read repeatedly.
- Application asks
- Observation asks
- is the method of writing.
- Duration of the action is an important “where” consideration.
- Psalm 1:1–3 speaks of the righteous man. Psalm 1:4–6 speaks of the unrighteous man. The structural devices used in these six verses is
- The book of uses the structural device of “question posed.” Here Paul leads his readers through his theological assertions by using questions.
- The principle of structure that briefly restates the main ideas presented is known as
- Observing important words, verb tense, command, etc. is part of observing the “what.”
- Interpretation asks
- Drawing conclusions based on your study of the facts is the process of .
- Careful observation guarantees accurate interpretation.
- Luke 1–3 weaves together the stories of John the Baptist and Jesus. This is the principle of structure known as
- The Bible was written across the continents of Asia, Europe, and Africa.
- This major fact would attempt to identify a point in the history of Israel or the church.
- When you read the passage with care you are reading .
- “Why” is a critical component in the process of observation.
- Hebrews 4:12 says, “For the word of God is living and active. Sharper than any doubled- edged sword, it penetrates even to dividing soul and spirit, joints and marrow; it judges the thoughts and attitudes of the heart.” This is an example of
- The question of purpose is two-sided since it addresses
- A word’s meaning is tied to the sentence by rules of grammar.
Set 2
- A word’s meaning is tied to the sentence by rules of grammar.
- The pivot point in the life of Kind David is when
- Which of the following is not one of the five C’s of interpretation?
- What is the third step in the process of observation?
- ________________ is simply the gathering of all the facts of who, what, where, and when.
- ___________________ brings meaning to the facts.
- _______________ is the goal of Bible study. It is not enough for us to understand Scripture; God wants us to be changed by it.
- In the step of interpretation, we are
- What is the second step in the process of observation?
- Observing a landmark can be an important part of observing the “where.”
- Which of the following is not one of the five C’s of interpretation?
- When you read the passage with care you are reading ____________.
- ______________ deals with the content of the Bible.
- Duration of the action is an important “where” consideration.
- This major fact seeks to identify all the principle characters in the passage.
- The book of ___________ uses the structural device of “question posed.” Here Paul leads his readers through his theological assertions by using questions.
- Observation asks
- Illustration introduces an idea followed by an example of it.
- _______________ is the method of writing.
- ______________ can be defined as the ministry of the Holy Spirit which makes clear the truth of the written revelation of the Bible.
- Since we are not eyewitness, historical considerations are only somewhat important because they are difficult to grasp.
- Drawing conclusions based on your study of the facts is the process of __________________.
- When observing the characters in a passage, the characters indirectly involved in the action are inconsequential.
- When you are observing a whole passage you should read the passage with care, record your initial impressions, and record the major facts.
- Application asks
- Luke 1–3 weaves together the stories of John the Baptist and Jesus. This is the principle of structure known as
- Words that can help to uncover the major facts are who, what, where, and which.
- When you read the passage with care you are reading ____________.
- Explanation introduces an idea that is the expanded or clarified.
- “Why” is a critical component in the process of observation.
Set 4
- When observing the characters in a passage, the characters indirectly involved in the action are inconsequential.
- _______________ is the method of writing.
- Words that can help to uncover the major facts are who, what, where, and which.
- Observation is simply knowing
- _______________ deals with the understanding or meaning of the inspired Word of God.
- Application asks
- What is the third step in the process of observation?
- Comparison is associating things that are opposite.
- Which of the following is not a principle to keep in mind when you ask questions of interpretation?
- Illustration introduces an idea followed by an example of it.
- The principle of structure where altering or exchanging certain elements in the text so that the reader is moving back and forth between several ideas is known as
- This major fact would attempt to identify a point in the history of Israel or the church.
- Since we are not eyewitness, historical considerations are only somewhat important because they are difficult to grasp.
- What is the second step in the process of observation?
- A word’s meaning is tied to the sentence by rules of grammar.
- When you read the passage with care you are reading ____________.
- In the step of interpretation, we are
- The gathering together of main ideas by the author in order to clarify his thoughts is known as summary.
- ______________ deals with the content of the Bible.
- In interpretation, stating the initial proposal based on the content allows you to test your hypothesis as your work through the other stages of interpretation.
- The question of purpose is two-sided since it addresses
- Observing important words, verb tense, command, etc. is part of observing the “what.”
- ___________________ brings meaning to the facts.
- In order to read a passage with care it should be read repeatedly.
- Galatians 6:7–8 says, “Do not be deceived: God cannot be mocked. A man reaps what he sows. The one who sows to please his sinful nature, from that nature will reap destruction; the one who sows to please the Spirit will reap eternal life.” This is an example of
- When stating your interpretive conclusion you do not need to consider your initial proposal.
- 1 Corinthians 7 and 8 uses the structural device of
- The principle of structure that briefly restates the main ideas presented is known as
- Which of the following is not one of the five C’s of interpretation?
- Interpretation asks
